Kenya: Leading Role in East African Community
Hong Kong Export Credit Insurance Corporation | 31 Dec 2015
Kenya: Leading Role in East African Community
Strengths
- Strategic location - logistical hub for the East African region
- Rich natural resources
- Large and young population
Challenges
- High poverty rate
- Weak economic fundamentals - twin deficits in fiscal and current accounts
- Security issue related to terrorist attack
|
Key Information
|
|
| Capital | Nairobi |
| Population | 44.9 million |
| Currency | Kenya shilling (1 KES = 0.0098 USD as of 19 October 2015) |
| Official language | English and Kiswahili |
| Form of state | Unitary republic |
| Major Merchandise Exports (% of total, 2013) | Major Merchandise Imports (% of total, 2013) |
| Tea (21.0%) | Industrial supplies (29.1%) |
| Horticulture (20.1%) | Machinery & other capital equipment (17.4%) |
| Coffee (4.7%) | Transport equipment (11.3%) |
| Top Three Export Markets (% of total, 2014) | Top Three Import Markets (% of total, 2014) |
| Uganda (11.8%) | India (23.4%) |
| Tanzania (7.7%) | China (21.3%) |
| Netherlands (7.5%) | UAE (7.6%) |
Source: Economist Intelligence Unit (www.eiu.com)
Political Trend
Kenya is a constitutional democracy with a bicameral parliament and executive president directly elected by voters. The inauguration of President Uhuru Kenyatta and Deputy President William Ruto in 2013 marked the official launch of decentralisation. The new government intends to push ahead with reforms, including trade liberalisation, privatisation and deregulation, in order to improve the business environment, thereby boosting growth and cutting poverty. Increased use of public-private partnerships and the roll-out of key infrastructure projects will facilitate the process. However, progress is likely to be uneven and subject to delay, including the passage of legislative reforms, because of public-sector capacity constraints and institutional turf wars.
Since late 2011, Kenya has seen an upsurge in violent terrorist attacks. The attacks had affected Kenya's tourism industry, which represented around 12% of GDP, as Western countries had issued travel warnings to their citizens. Official data from Kenya showed that the number of foreign visitors fell 18.3% for the first eight months of 2015.
Economic Trend
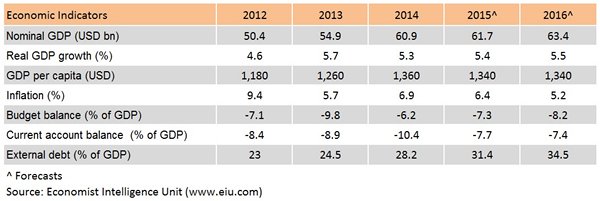
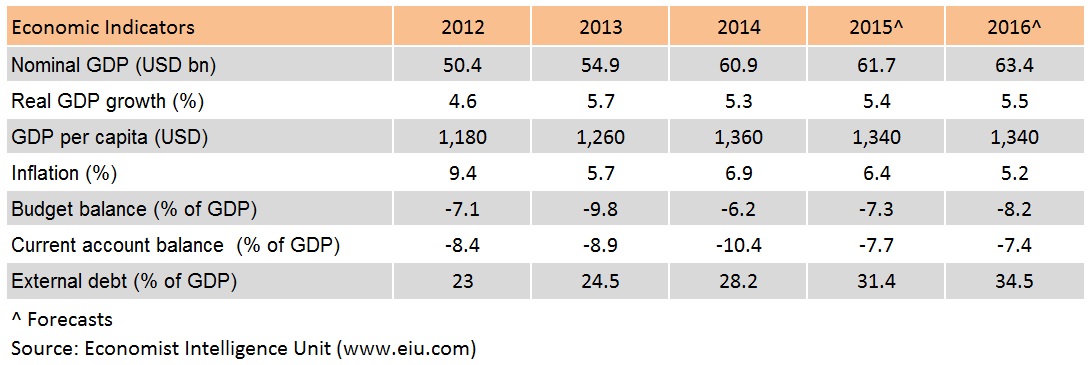
Kenya is emerging as one of Africa’s key growth centres and is poised to become one of the fastest growing economies in East Africa, supported by lower energy costs, investment in infrastructure, agriculture and manufacturing. Expansion was relatively broad-based with all sectors posting growth except for tourism, which shrank by 0.8% yr/yr. Economic performance is expected to remain solid, though the uncertainty facing global currencies is causing volatility in the domestic money and foreign exchange markets.
Kenya is East African Community’s (EAC's) biggest and most advanced economy, and serves as the logistical hub for the EAC's other landlocked nations. According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) World Investment Report 2015, Kenya’s FDI inflows rose 95% to a record high of US$989 million in 2014, with FDI flows coming from a wide variety of sources, including the US, Europe, key Asian economies and South Africa. Investors are attracted by Kenya’s relatively diverse economy, pro-market policies and brisk growth in consumer spending.
Kenya maintains wide deficit in both of its budget account and current account, making its economy prone to market capital flow. Meanwhile, Kenya’s current account deficit remains structurally high (around 7-8% of GDP) on the back of low-value exports - mostly tea and horticulture, and strong imports of both capital and consumer goods. Yet, the situation is expected to improve in the medium term as the recent discoveries of oil, gas and minerals in Kenya could do a favorable impact on the country’s external fiscal prospects.
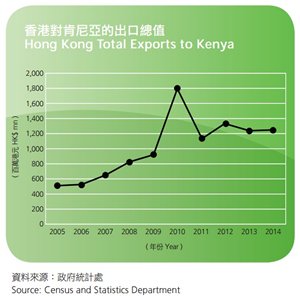
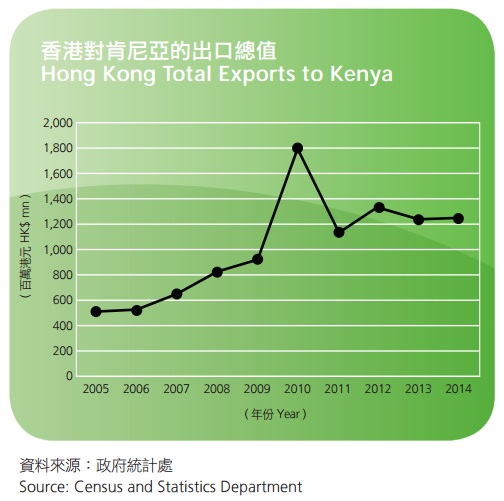
Hong Kong – Kenya Trade
Total exports from Hong Kong to Kenya increased by 0.2% from HK$1,249 million in 2013 to HK$1,251 million in 2014. The top three export categories to Kenya were: (1) telecommunications, audio & video equipment (+8.8%), (2) clothing & clothing accessories (+29.9%), and (3) textiles (-16.7%), which represented 82.2% of total exports to Kenya.
ECIC Underwriting Experience
The ECIC imposes no restrictions on covering Kenyan buyers. Currently, the insured buyers in Kenya are mainly small and medium sized companies. For 2014, the number of credit limit applications on Kenya decreased by 6.8%, while the amount of credit limit applications and insured business increased by 7.1% and 232.3% respectively. Major insured products were chemical products, electronics, and toys, which represented 96.6% of ECIC’s insured business on Kenya. The Corporation’s underwriting experience on Kenya has been satisfactory, with no claim payment or payment difficulty case reported from October 2014 to September 2015.
| Content provided by |  |